Probability
> If an experiment has x equally likely outcomes of which y outcomes are favourable to event A, then the probability of event A is: P(A)= x/y.
Here is one example of questions we did on class (#8).
>On the game board shown below, you can move the game piece diagonally forward.

a) Determine the number of different pathways from the game piece to each of the squares on the other side of the board.
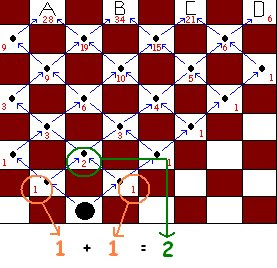
>There are 28 pathways to A.
>There are 34 pathways to B.
>There are 21 pathways to C.
>There are 6 pathways to D.
b) Assume that a player is equally likely to go left or right on each move.
What is the probability he will land on:
i) square A? ii) square C?
ANSWER:
Total number of pathways to exits= 28 + 34 + 21 + 6 = 89
i) 28/89 = .315 ii) 21/89 = .236
> The next scribe is just_in.... ~(_8(])

No comments:
Post a Comment